Introduction
An ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) system is a strategic tool for manufacturing organizations to optimize operations and drive profitable growth. Production and manufacturing operations are complex, requiring a resilient, scalable, and comprehensive ERP that covers essential functions such as production planning, inventory management, quality control, and machinery maintenance. For manufacturing companies seeking an ERP system, Odoo ERP, with its modular architecture and customization options, stands out as an excellent choice. From initial planning to end-to-end deployment and post-implementation optimization, this complete guide provides a comprehensive roadmap for implementing Odoo ERP in your manufacturing business.
What You Will Learn
1) Appreciating Odoo ERP for Manufacturing
Production Planning
- Optimized Schedules: Create detailed production schedules to reduce downtime and enhance manufacturing efficiency.
- Resource Management with MPS and MRP: Ensure all materials, labor, and machinery are ready when needed to avoid production delays.
- Capacity Planning: Maximize production line efficiency without overburdening resources.
Inventory Management
- Real-Time Tracking: Monitor inventory levels in real-time, including raw materials, work-in-progress (WIP), and finished goods.
- Automated Reordering: Set automated reorder points to maintain ideal inventory levels, preventing both excess stock and stockouts.
- Warehouse Management: Manage multiple warehouses, track stock movements, and maintain accurate inventory records.
Quality Control
- Quality Inspection: Implement quality control checkpoints to ensure products meet specifications before progressing to the next stage.
- Quality Alerts: Receive notifications of any quality issues swiftly.
- Traceability: Ensure full traceability from raw materials to finished goods for quality concerns.
Overall Efficiency
- Multi-department Integration: Connect production, inventory, sales, and other departments into a single streamlined process.
- Accurate Data: Centralize data to avoid errors and ensure real-time access across departments.
- Informed Decision-Making: Utilize live data and advanced analytics for continuous operational improvements.
2) Preparing for Implementation
Assessing Needs
- Current State Analysis: Examine current processes, systems, and pain points to identify areas for improvement.
- Gathering Requirements: Collaborate with stakeholders to understand needs and expectations for the new ERP system.
Setting Goals
- Specific Objectives: Define clear project objectives, such as reducing production turnover times, improving inventory accuracy, or enhancing quality control.
- KPIs: Develop key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure ERP implementation success.
Implementation Team
- Composition: Include relevant stakeholders from across the organization (production, IT, finance, etc.).
- Roles and Relationships: Establish clear roles and responsibilities for project managers, process owners, and technical experts.
3) Choosing the Right Modules
Module Specific for Manufacturing
- Manufacturing: Manage production orders, bills of materials (BOM), work centers, and routings.
- Inventory: Handle stock levels, warehouses, and logistics.
- Purchase: Streamline procurement processes, manage suppliers, and control purchase orders.
- Quality: Implement quality checks, manage quality alerts, and ensure standards compliance.
- Maintenance: Schedule and perform maintenance activities to minimize downtime and ensure equipment reliability.
Selecting Modules
- Fit for Purpose: Choose modules that best complement your business processes.
- Scalability: Ensure modules can scale with your growing business.
- Customization: Assess the level of customization required to match specific business needs.
4) Design of Implementation Process
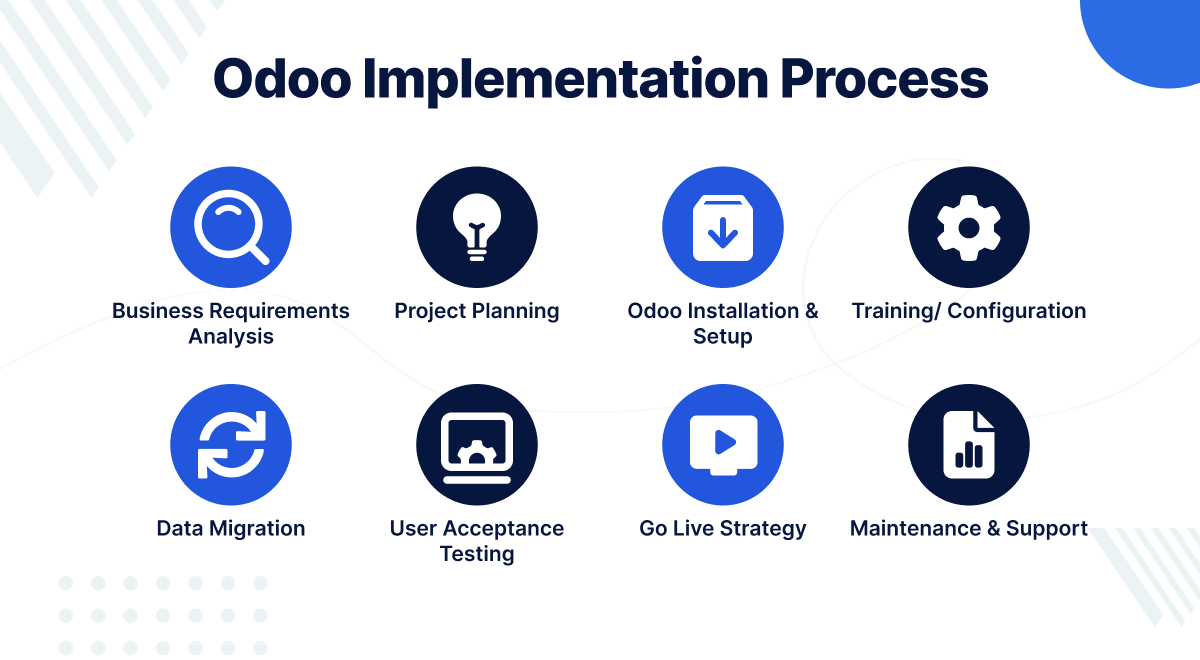
Implementation Plan
- Detailed Timeline: Develop a precise timeline with milestones and deadlines for each phase.
- Resource Allocation: Allocate personnel, budget, and time to ensure each phase is adequately resourced.
Project Management
- Project Management Tools: Use Gantt charts and task management software to manage timelines and issues.
- Risk Management: Identify potential risks and devise strategies for mitigation.
5) Data Migration and System Configuration
Data Migration
- Data Cleaning: Streamline and clean data to ensure only pertinent information is migrated.
- Data Migration Tools: Use tools to transfer data from legacy systems to Odoo ERP.
- Data Verification: Validate data accuracy and completeness after migration.
System Configuration
- Settings Configuration: Customize Odoo settings to mirror your company's workflows, create user roles, and configure system parameters.
- Customization: Tailor the software to fit your business needs without changing existing business processes.
6) Customizing Odoo ERP
Customization Options
- Custom Fields: Add custom fields to capture unique data points.
- Workflows: Develop workflows to automate and standardize business operations.
- Custom Reports: Create custom reports for detailed decision-making insights.
Leveraging Flexibility
- Customizability: Grow and adapt Odoo to suit evolving business needs.
- Integration: Extend Odoo ERP features by integrating third-party applications and services.
7) Training and Change Management

Training Programs
- Comprehensive Training: Provide detailed training materials like user manuals, tutorial videos, and FAQs.
- Role-Specific Training: Ensure employees understand module-specific functions and best practices.
Change Management
- Effective Communication: Clearly communicate the benefits and objectives of ERP implementation to all stakeholders.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Involve key stakeholders to encourage adoption and support.
- Ongoing Support: Offer continuous support and resources to help users transition smoothly.
8) Testing and Go-Live
Testing
- Deployment Plan: Conduct system testing, unit testing, functional testing, integration testing, and user acceptance testing.
- Pilot Testing: Test with a small group of users to gather feedback and make necessary adjustments.
Go-Live Preparation
- Readiness Assessment: Confirm systems, processes, and users are ready for go-live.
- Detailed Checklists: Create step-by-step checklists to ensure a smooth transition.
Minimizing Disruption
- Contingency Plans: Develop plans to address potential issues during go-live.
- Service Desk: Establish support teams to assist users during the transition.
9) Optimizing After Launch
Continuous Improvement
- Regular Reviews: Monitor system performance and user feedback to identify areas for improvement.
- Optimization Strategies: Implement strategies to enhance system efficiency and effectiveness.
User Feedback
- Feedback Loops: Create channels for users to provide feedback on system performance.
- Action Plans: Develop plans to address user feedback and improve system functionality.
Future Updates
- Planned Updates: Schedule future updates and extensions to keep the system current with industry standards.
- Scalability: Ensure the system can scale with your growing business.
10) Success Stories and Case Studies
Real-World Examples
- Success Stories: Highlight successful Odoo ERP implementations in other manufacturing companies.
- Best Practices: Apply lessons learned from these case studies to your own implementation.
Conclusion
Deploying Odoo ERP in a manufacturing unit centralizes all operations, making business processes smoother and fostering growth. This guide helps navigate the challenges of ERP implementation, ensuring a seamless transition to a more efficient and effective manufacturing operation.